Human trafficking : Third-Largest Industry in the World
Human trafficking known as a modern form of slavery. Globally, one in every three victims is a child.Poverty and weak legal systems are among the leading causes of human trafficking.

Human Trafficking: The Third Largest Industry in the World
Human trafficking is known as a modern form of slavery which is affecting people globally. According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), around 24.9 million people are trapped by human traffickers each year through various means. Most of their targets are women and children, with female victims being the primary focus.
According to 2018 statistics, out of every ten victims, five were women and two were girls. Globally, one in every three victims is a child. Traffickers commonly use land and sea routes to smuggle people across borders. Countries like India, Pakistan, China, and North Korea are among the most affected by human trafficking.
UN Definition of Human Trafficking
According to the United Nations:
“Human trafficking shall mean the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring or receipt of persons, by means of threat, force, coercion, abduction, fraud, deception, abuse of power, or giving payments or benefits to a person in control of the victim, for the purpose of exploitation.”
There are three main elements of human trafficking:
The Act (What is done?) Recruitment, transportation, harboring, and receipt of persons.
The Means (How is it done?) Threats, force, coercion, abduction, deception, fraud, abuse of power or vulnerability, and promises of jobs or marriage.
The Purpose (Why is it done?) Exploitation, including prostitution, sexual exploitation, forced labor, slavery, and organ removal.

Poverty and weak legal systems are among the leading causes of human trafficking. After the COVID-19 pandemic, trafficking evolved due to widespread job losses and restricted movement, leading to a shift toward online trafficking.
Traffickers now use social media platforms to post fake job ads—especially for jobs related to modeling or domestic work-to lure victims. They also use social platforms to connect with other traffickers. The dark web is frequently used to advertise and sell trafficked individuals, particularly for sexual exploitation. These platforms are difficult to track and shut down because they rely on cryptocurrencies and decentralized systems.

Traffickers have also moved into online gaming chatrooms and use coded language to communicate. A rising concern is cybergrooming, where adults manipulate children online to gain control over their lives and exploit them.
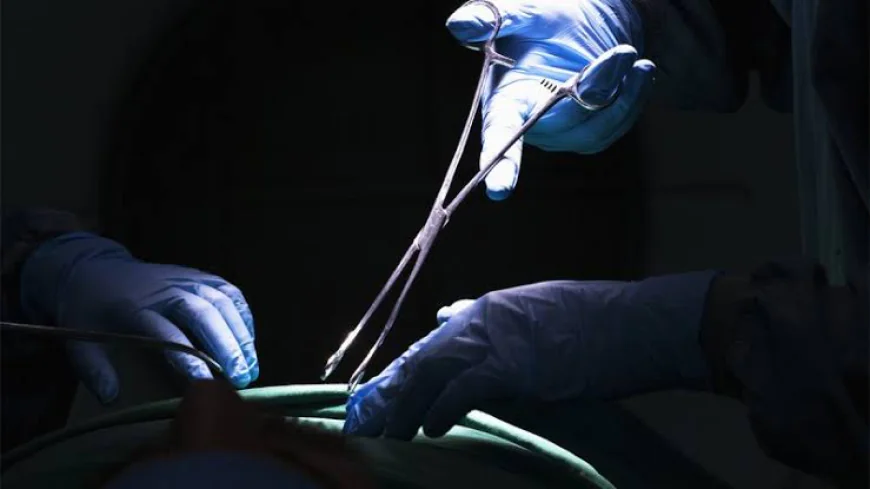
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 10% of the global demand for kidney transplants is fulfilled through the illegal organ trade, which is closely linked to human trafficking. Traffickers operate through brokers who supply organs as needed. The cost of a kidney on the black market can range from $10,000 to $200,000, making it a highly profitable illegal business.
The Ukraine-Russia war has significantly increased the risk of human trafficking, especially for women and children. Displacement due to conflict makes people more vulnerable, and traffickers exploit their desperation for safety. Many fleeing the violence face forced labor and sexual exploitation in neighboring countries. According to the International Organization for Migration (IOM, 2022), there has been a notable rise in trafficking cases since the beginning of the war.

Traffickers use both physical and psychological torture to control their victims. This includes sexual assault, beatings, threats to family members, and malnutrition. Victims are often drugged to dull their senses and prevent escape. They are kept in isolation, cutting them off from any support systems. These experiences leave deep psychological scars, making recovery and reintegration extremely difficult.
To overcome this global crime requires awareness and action at all levels:
Community awareness campaigns should be launched to educate people about human trafficking.Media literacy must be promoted so people, especially young people, can navigate the internet more safely.Law enforcement agencies need to act more efficiently; creating laws is not enough; implementation and justice delivery are crucial.Support systems for survivors must be improved to ensure their recovery and reintegration.


